Glass Worms are a type of marine worm that inhabits the North Atlantic Ocean. Their transparent body and bristle-like appendages make them an important part of the food chain for various marine animals, including fish and whales.
Due to their nutritional value, people often collect and sell Glass-Worms as bait for fishing. You can find them in shallow waters along the coastline or farther to sea. These worms play a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems in the ocean and are an essential component of marine biodiversity.
Here we will dive deep into the details of Glass-Worms. From their appearance and behavior to their life cycle and collection. So if you’re curious about these tiny creatures, keep reading to learn all there is to know about Glass-Worms.

Discussion On- Glass Worms
Glass Worms, phantom midge larvae, or glassworms are small, translucent worms in freshwater environments worldwide. They attach themselves to vegetation and feed on small organisms like Daphnia, mosquito larvae, and gnat larvae. Fish commonly use glass-worms as a food source and are handy as fish food in aquariums. Below we discuss more in detail.
Appearance
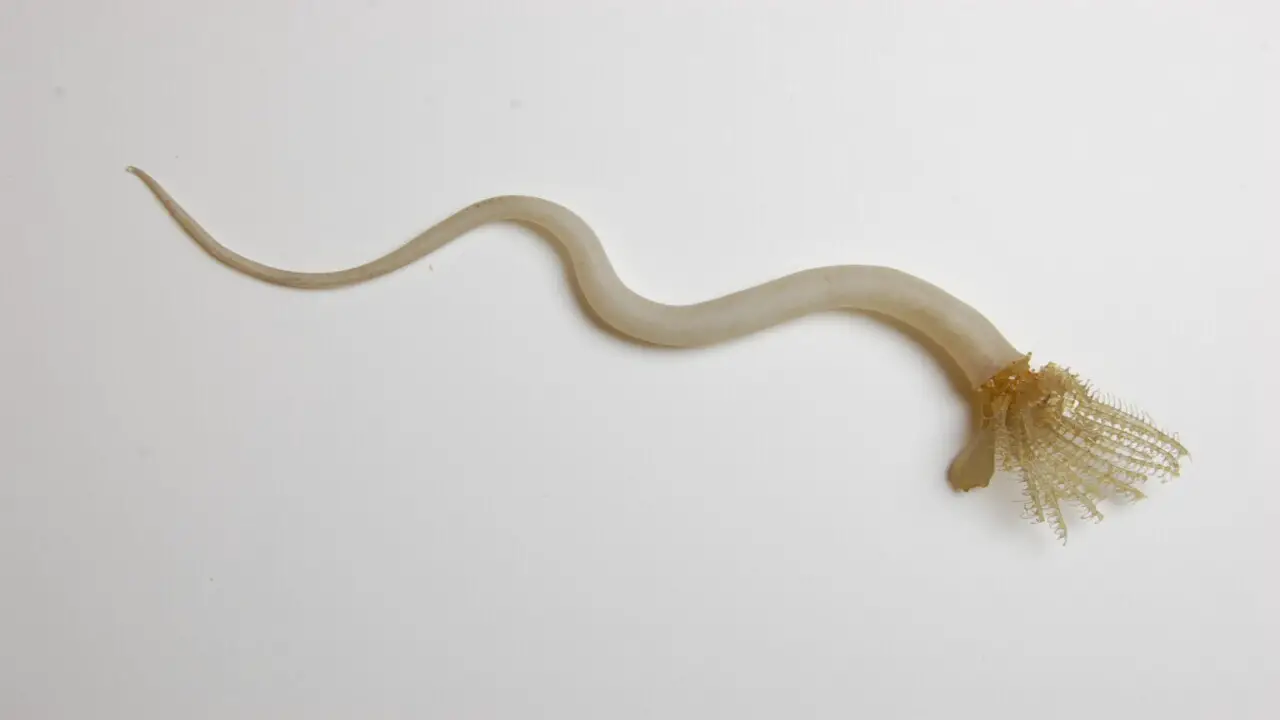

Glass-Worms, phantom midge larvae, are fascinating creatures found in freshwater bodies. They have a transparent body with small bristles and can grow up to 2 inches long. Their translucent appearance makes them attractive bait for fishing. Under a microscope, their intricate body structure and vibrant colors become visible. Glass-Worms are captivating and useful, providing valuable insight into aquatic life. Take a moment to appreciate their unique beauty.
Behaviour
Glass-Worms, phantom midge larvae, are fascinating aquatic insects in lakes and ponds. They swim and crawl in a mesmerizing wavelike motion, making them attractive to fish and aquarium owners.
These translucent worms play an important role in the ecosystem as a food source for aquatic animals. Studying their behavior helps researchers and hobbyists understand their ecological roles and contributes to freshwater ecosystem conservation. By unraveling their secrets, we can appreciate the contributions of these creatures to our natural world.
Life Cycle
The life cycle of Glass-Worms is a fascinating process to observe. Glass-Worms, phantom midge larvae, start their life as eggs laid in freshwater bodies. These eggs hatch into tiny larvae, which then go through several stages of growth and development. During these stages, the Glass-Worms feed on organic matter and algae in the water.
As they grow, they molt their exoskeletons multiple times before reaching their final stage as mature larvae. At this point, the Glass Worms undergo a transformation known as pupation, during which they encase themselves in a cocoon-like structure. Inside this structure, they develop into adult midges. Once fully developed, the adult midges emerge from the cocoon and take flight to reproduce and continue the life cycle of Glass-Worms.
Collection
Glass-Worms are popular among anglers and researchers. They can be found in freshwater lakes and rivers across North America, Europe, and Asia. To collect them, a fine mesh net or suction sampler is handy. Proper handling is crucial to maintain their quality and viability. Careful handling ensures their survival and avoids unnecessary stress or damage.
Collecting Glass-Worms provides anglers with bait and enables scientists to study their behavior, biology, and ecology. Researchers gain insights into their role in the ecosystem and interactions with other organisms, contributing to understanding freshwater environments.
Collecting Glass-Worms involves using specialized equipment. Anglers and researchers rely on proper techniques for these aquatic larvae. The collection of Glass-Worms plays an important role in both recreation and research.
Species
Glass-Worms, scientifically known as Chaoboridae, are midge flies that play a significant role in the aquatic ecosystem. They are recognized by their clear or translucent bodies and lack of legs. Glass-Worms are vital food sources for fish and other aquatic animals, contributing to a healthy ecosystem. Their lifecycle begins as eggs, hatching into larvae called phantom midges or glassworms.
These larvae go through instars and pupa stages before becoming adults. Glass-Worms are commonly found in freshwater lakes and rivers and can be collected using nets or suction samplers. Anglers use them as bait, while scientists utilize them for experiments. Overall, Glass-Worms are fascinating creatures with practical fishing and scientific research applications.
References
Glass-Worms, or Tubifex worms, are commonly used as fish food and can be found in freshwater environments. They are important water quality indicators and are vital food sources for fish and other aquatic animals. Glass-Worms have clear bodies, no legs, and a long segmented appearance.
Anglers collect them for bait, while scientists use them for research. Proper collection techniques and handling are crucial to maintain their quality. Studying Glass-Worms contributes to understanding their behavior, life cycle, and influence on ecosystems. They are significant in fields related to water quality and aquatic organisms.
How To Identify Glassworms?
Glassworms are aquatic insect larvae commonly found in standing freshwater sources such as ponds and lakes. They can be easily identified by their transparent bodies and the presence of prolegs, which are specialized feeding apparatus that they use to grasp prey.
Glassworms play an important role in freshwater ecosystems, serving as a food source for many fish species. In addition, these small, transparent worms have been studied for their unique ability to regenerate damaged body parts and may hold potential for medical research in the future.
How To Care For Glass-Worms
To ensure Glass-Worms’ well-being, provide them with a clean and oxygen-rich aquatic environment. These transparent larvae, such as small aquatic invertebrates and fish food, need proper nutrition. Monitor water temperature and pH levels regularly to create a healthy habitat. Glass-Worms are valuable for aquariums as they serve as abundant food for fish.
Depending on their number and size, they can be kept in tanks of various sizes. Glass-Worms, or phantom midges or chorus, are inch-long larvae with transparent bodies and prolegs at the end of their abdomen. They thrive in freshwater sources like ponds and lakes.
By providing clean water, a balanced diet, and suitable tank sizes, you can care for Glass-Worms effectively. Regular monitoring and care continue to play an important role in the food chain, benefiting aquarium enthusiasts and the fish that rely on them.
Benefits Of Glass-Worms
Glass-Worms are a nutritious and convenient fish food for aquariums. These transparent larvae, phantom midge larvae or Chironomidae, offer high protein content, vitamins, minerals, and amino acids that promote fish health. They also improve water quality by consuming organic waste and reducing harmful substances. Here are a few more benefits of Glass-Worms.
- Glass-Worms are a nutritious food source for fish, reptiles, and amphibians.
- They are high in protein and contain essential amino acids.
- Glass-Worms can help enhance the growth and development of aquatic pets.
- They also stimulate natural feeding behaviors in fish and other aquatic animals.
- Glass-Worms are readily available and can be easily stored for future use.
- They serve as a great alternative to live or frozen foods for pet owners who prefer convenience.
- Due to their translucent appearance, Glass-Worms can be visually appealing to both pets and pet owners.
How To Get Glass-Worms?
To obtain Glass-Worms, you can visit fishing bait shops or purchase them online from reputable retailers. They are typically sold frozen or refrigerated to preserve their freshness. Alternatively, some fishers collect Glass-Worms from natural sources such as streams and rivers. Remember to adhere to local fishing regulations when using Glass-Worms as bait.
Things To Keep In Mind If You Have Glass-Worms
To manage Glass-Worms in your aquarium, keep these tips in mind. Glass-Worms are harmless but can become a nuisance. Maintain a clean tank with regular maintenance and filtration. If their population becomes excessive, feed them to other aquatic pets as protein. Consult a professional if needed. By following these tips, you can maintain a healthy aquarium environment while managing the presence of Glass-Worms effectively.
Conclusion
Glass Worms are fascinating creatures that play a vital role in aquatic ecosystems. Their transparent appearance and unique behavior make them a captivating subject for study and observation. It is important to understand their life cycle, identify them correctly, and provide appropriate care if you choose to keep them as pets.
Glass-Worms offer several benefits, such as being a nutritious food source for fish and a natural indicator of water quality. If you want Glass-Worms, purchasing them from reputable sources and following proper handling and maintenance guidelines is recommended. We can contribute to preserving and understanding our aquatic environments by appreciating and respecting these delicate organisms.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Do Glass-Worms Turn Into?
Glass-Worms, the larval stage of a fly species, transform into adult midges after going through their pupal stage. The adult midges have a short lifespan of one to two days and play a crucial role in aquatic ecosystems as a food source for fish and other animals.
What Do Glassworms Eat?
Glassworms are aquatic insects with a diet primarily consisting of small, live prey such as mosquito larvae, daphnia, and other small aquatic organisms. In captivity, they can be fed fish food flakes or freeze-dried bloodworms.
Are Glass-Worms Good For Fish?
Glass-Worms are a popular fish food choice for small and medium-sized fish. They are rich in protein and provide essential nutrients for fish growth. Larger fish can also enjoy Glass-Worms as a supplement or treat.
What Are Glass-Worms, And Where Are They Found?
Glass-Worms, or bloodworms, are the transparent larvae of chironomid midges. They are commonly found in freshwater habitats like ponds and lakes and are often used as bait for fishing or aquariums
Are Glass-Worms Harmful To Humans Or Pets?
Glass-Worms, marine worms handy as fishing bait, are not harmful to humans or pets. Despite their intimidating appearance, they lack stingers or venomous bites.

Aquarium passion is all about connecting with the aquatic life and providing education to the public on the importance of these creatures. We showcase a wide variety of marine life through our exhibits as well as working with schools to provide unique learning opportunities for students of all ages.