The Pike topminnow, also known as the blackspotted Topminnow, is a small freshwater fish native to North America.
Despite their small size, these fish play an important role in their aquatic ecosystem as they are popular for consuming mosquito larvae and other small invertebrates. They can be found in various freshwater habitats, including streams, rivers, and ponds.
However, due to habitat loss and degradation, these fish populations have been declining in recent years. As a result, conservation efforts are being made to protect and restore their natural habitats. Here, we will provide a comprehensive overview of the Pike-topminnow, including its physical characteristics, habitat preferences, and behavior.
We will also explore the current threats facing the species, as well as the conservation efforts being undertaken to protect it. Additionally, we will discuss the importance of preserving freshwater ecosystems’ biodiversity and the Pike-topminnow’s role in maintaining this delicate balance.

About This Fish
The pike-topminnow (Poecilurichthys piquitus) is a species of freshwater fish in the family Fundulidae, endemic to the eastern United States. It is a small fish, typically less than 2 inches long, found in shallow, rocky streams and pools.
The pike-topminnow feeds on small aquatic invertebrates and is an important prey species for larger fish and birds. Habitat loss and degradation have led to the current listing of the species as endangered.
Importance Of Studying Pike-Topminnow
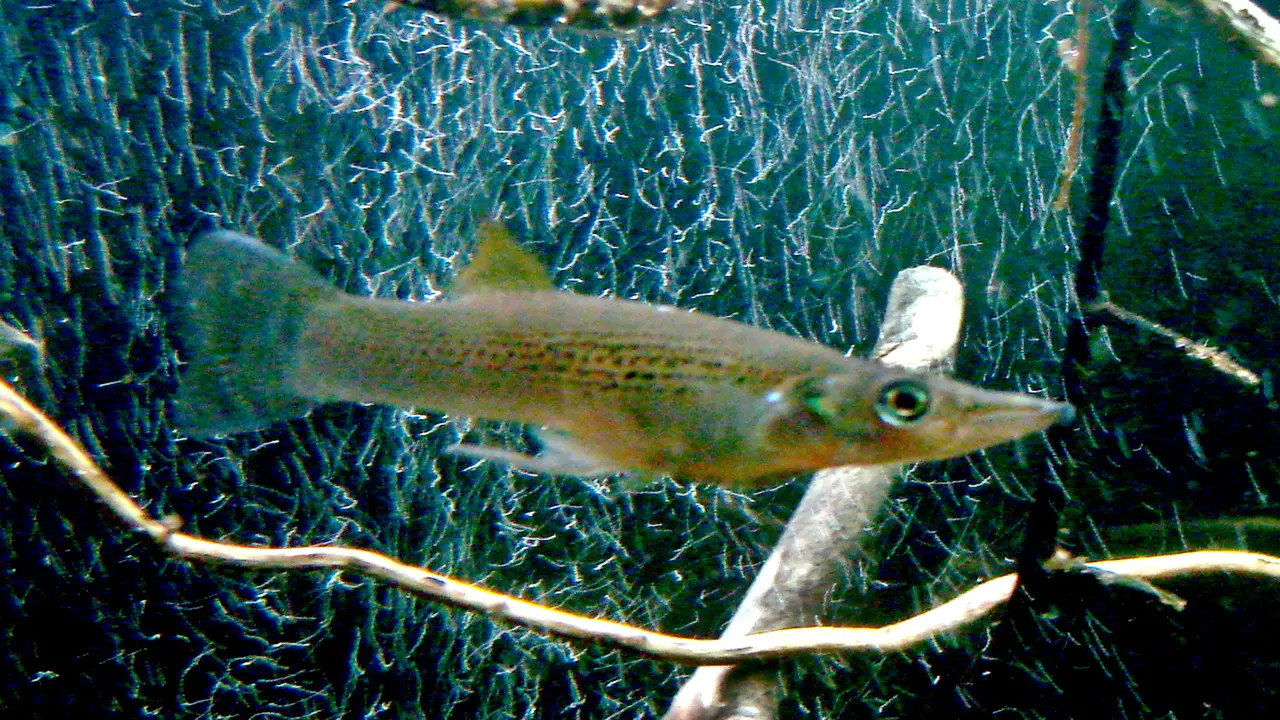

The pike-topminnow, also known as the pike killifish, is a small freshwater fish native to North America. It is an important species to study because it indicates the health of aquatic ecosystems. Pike-topminnows are sensitive to changes in water quality and habitat conditions, so their presence or absence can indicate whether an ecosystem is healthy.
They also play an important role in the food chain, serving as prey for larger fish and birds. Understanding the ecology and behavior of pike-topminnows can help managers make informed decisions about protecting and restoring aquatic ecosystems.
Physical Characteristics Of Pike Topminnow – Full Discussion
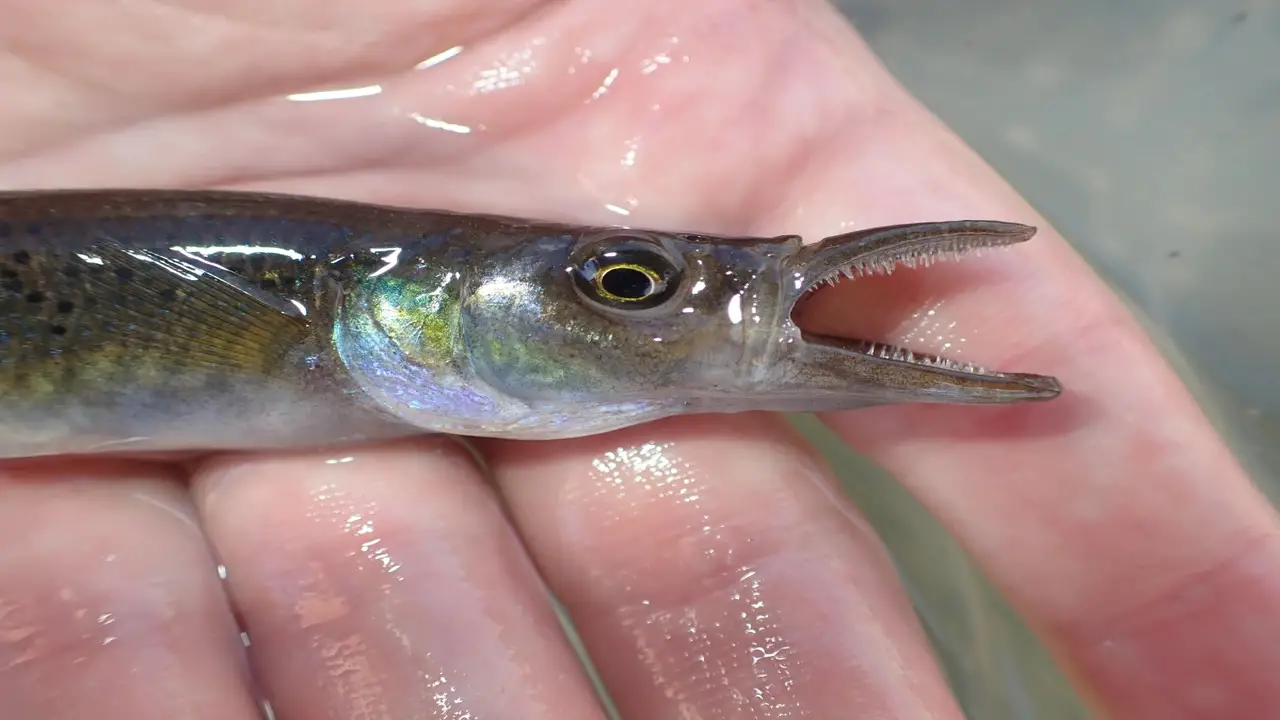

The pike-topminnow, also known as the pike killifish, is a small freshwater fish in North America. It has a slender, elongated body with a pointed head and a flattened belly. The pike- topminnow’s coloration is typically brown or olive on the back, with a lighter color on the sides and a white or yellowish belly.
It has a long dorsal fin and a forked tail. The average size of a pike topminnow is 2-3 inches long. They are popular to be active swimmers and can be found in slow-moving streams, ponds, and marshes.
Size And Shape
The pike-topminnow is a small freshwater fish typically growing 2-3 inches long. It has a cylindrical body shape, a pointed head, and a small mouth. The dorsal fin is on the back of the fish and is tall and pointed, while the anal fin is on the underside of the fish and is shorter and rounded. The body is typically brown or olive with darker mottling or banding, and the fins are often bright orange or yellow.
Coloration And Markings
They are known for their distinct coloration and markings, varying depending on their habitat and geographic location. Generally, pike-topminnows have a dark greenish-brown back with a lighter-colored belly.
They also have a series of dark vertical bars that run along their sides, ranging from light brown to black. The dark blotch near their dorsal fin is prominent, and their fins often have white edges. These markings help to camouflage them in their natural environment, making them less visible to predators.
Habitat And Distribution
The pike-topminnow (Notropis lucidus) is a freshwater fish native to North America, specifically found in the Great Lakes region and the Mississippi River basin. Clear, cool streams and rivers with rocky or sandy bottoms typically hold them.
Habitat loss and degradation caused by pollution, damming of rivers, and agriculture threaten the pike-topminnows species. People are making efforts to conserve their populations, including habitat restoration and reintroduction programs.
Life Cycle And Behavior Of Pike-Topminnow
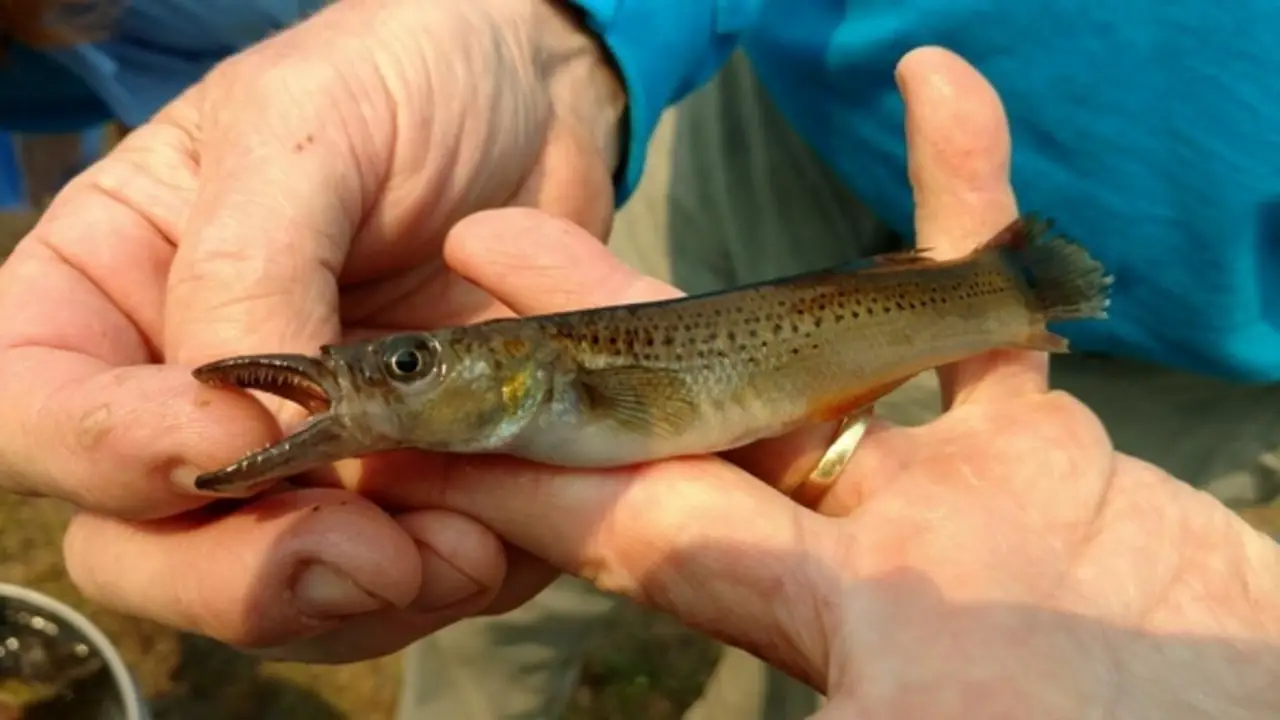

The pike-topminnow’s life cycle typically begins in the spring, when males and females spawn in shallow water. The eggs hatch within a week and the fry feed on zooplankton for the first few weeks of their lives.
As they grow, pike-topminnows begin to feed on aquatic insects, small crustaceans, and other small fish. They typically reach maturity at around one year of age and can live up to three years in the wild.
Behaviorally, pike-topminnows are known for their aggressive feeding behavior and often attack prey much larger than themselves. They are also known to be territorial and will defend their breeding and feeding areas from other fish.
Reproduction And Spawning
Reproduction and spawning in pike-topminnow (Lucania goodei) typically occur from April to August, with peak activity in May and June. Males compete for females by displaying bright colors and performing courtship dances.
Females lay their eggs in nests, which males guard. The eggs hatch in about a week, and the fry feed on plankton until they can eat larger prey. Pike- topminnow are livebearers, meaning the eggs hatch inside the female, and she gives birth to live young. However, some populations of pike-topminnow in the wild still exhibit egg-laying behavior.
Feeding Habits
The pike-topminnow is a carnivorous fish that primarily feeds on small fish, insects, and crustaceans. They are opportunistic predators and will eat whatever prey is available in their habitat.
Various factors, including water temperature, water clarity, and the availability of prey influence the feeding habits of pike-topminnows. They are active predators and often hunt during the day and at night. During winter, they may slow down their feeding activity due to reduced metabolism and colder water temperatures.
Migration Patterns
The pike-topminnow is a small freshwater fish native to North America. It is popular for its migratory behavior, triggered by water temperature and quality changes. During the breeding season, which typically occurs in the spring and summer months, pike-topminnows travel to shallow water areas to spawn.
After spawning, the adults and young fish migrate to deeper water habitats to feed and grow. The migration patterns of pike-topminnows are important to understand for conservation efforts, as water quality or habitat changes can disrupt their natural behavior and affect their populations.
Threats To Topminnow Populations
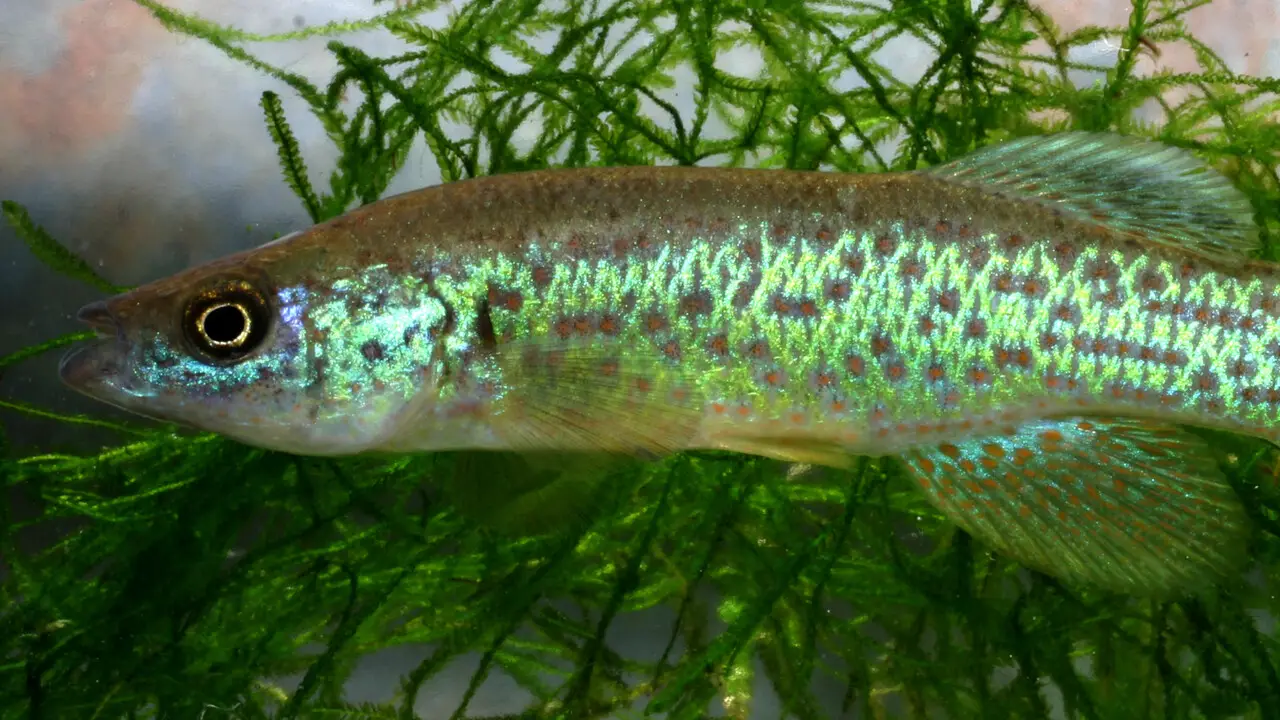

The pike-topminnow species of fish is found in North America, especially in the Great Lakes region. Threats to their populations include habitat loss and degradation, water pollution, predation by non-native species, overfishing, and climate change. Invasive species such as the round goby and zebra mussel compete with pike-topminnows for food and habitat.
In contrast, pollution and habitat destruction can reduce the quality of their breeding and feeding grounds. Overfishing and climate change can also impact their populations by reducing their numbers and altering their behavior. Conservation efforts such as habitat restoration, pollution control, and regulating fishing practices can help protect pike-topminnow populations from these threats.
Habitat Loss And Degradation
This small fish species primarily inhabits clear, shallow streams and wetlands with slow-moving water and dense vegetation. However, due to human activities such as urbanization, agriculture, and damming, many of these habitats have been destroyed or altered, leading to a decline in the pike-topminnow population.
In addition, water pollution and the introduction of non-native species have further threatened their survival. Conservation efforts such as habitat restoration and monitoring of populations are crucial in protecting the pike-topminnow and ensuring its continued existence in the wild.
As Non-Native Species
The introduction of non-native species can have a significant impact on native ecosystems and wildlife. Humans introduced the non-native species, pike-topminnow, to various bodies of water throughout North America. It is a predatory fish that can outcompete native species for resources and disrupt the balance of the ecosystem.
Introducing non-native species is often unintentional, such as through the release of aquarium pets or the accidental transport of species through shipping and trade. However, it is important to be aware of the potential consequences and take measures to prevent the introduction of non-native species to new environments.
Pollution And Water Quality Issues
These are some of the biggest threats facing the pike-topminnow population. This species is highly sensitive to changes in water quality, particularly regarding pH levels and oxygen content. Agricultural runoff, industrial waste, and sewage discharge can all contribute to water pollution, devastatingly affecting the pike-topminnow and other aquatic organisms.
In addition, the pike-topminnow’s habitat is often degraded due to development and urbanization, which can lead to stream channelization and erosion. Conservation efforts that focus on improving water quality and restoring degraded habitats are crucial for the survival of the pike-topminnow and other vulnerable aquatic species.
Conservation Efforts For Pike-Topminnow
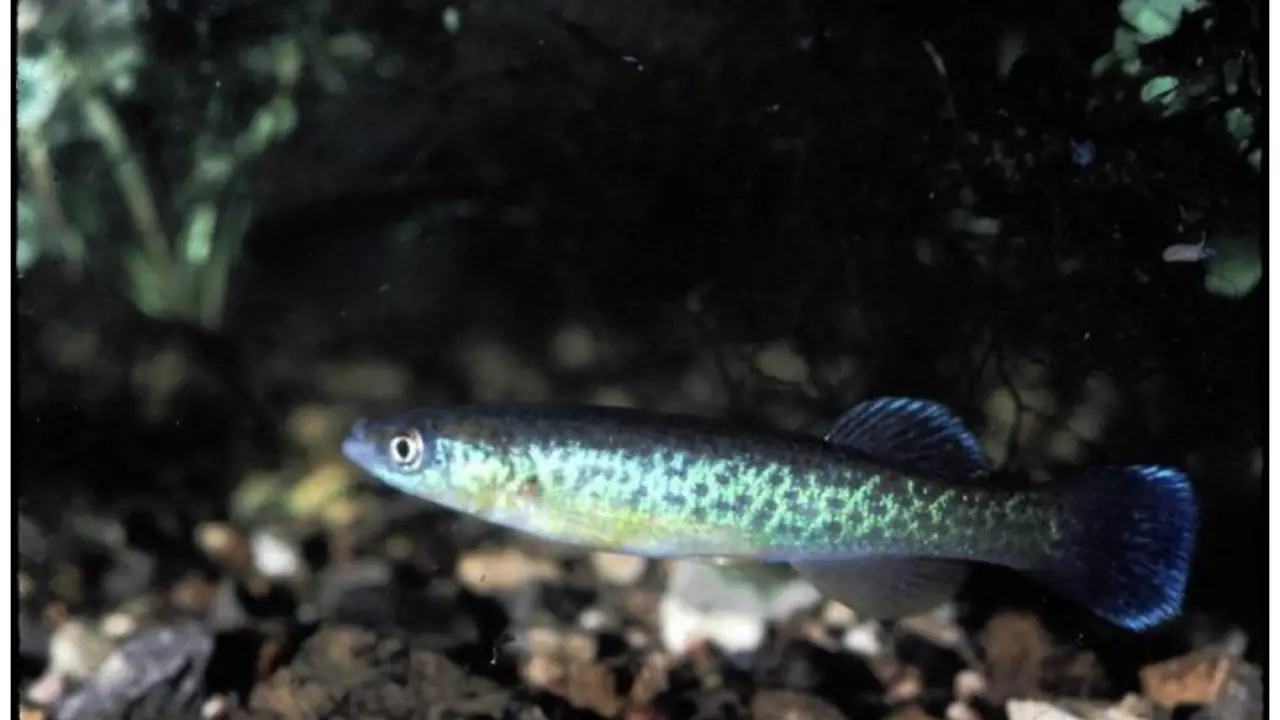

The pike-topminnow (Poecilurichthys piquitus) is a species of fish found in the United States. The species has experienced a decline in population due to habitat loss, pollution, and the introduction of non-native species.
Conservation efforts for pike-topminnow include monitoring populations, habitat restoration, and invasive species removal. Some groups are also working to raise awareness about the importance of conserving this species and its habitat.
Legal Protections And Regulations
Eligible steps are in place to protect the pike-topminnow and its habitat. The species is protected under the Endangered Species Act, and several conservation efforts are underway to restore their populations. Additionally, the Clean Water Act helps regulate water quality and pollution levels, which can significantly impact the health and survival of pike-topminnows and other aquatic species.
Biologists and government agencies are also working to identify and protect critical habitat areas for the species, such as clean and well-oxygenated streams and wetlands. The pike-topminnow’s plight underscores the importance of protecting and conserving our planet’s freshwater ecosystems and the species that depend on them.
Habitat Restoration And Management
Habitat restoration and management refer to improving, maintaining, and preserving natural habitats that support various species of plants and animals. In the pike- topminnow context, habitat restoration, and management may involve improving water quality, restoring aquatic vegetation, and enhancing stream flow to support the species.
The pike-topminnow is a small fish species that is native to North America. It is found in freshwater habitats like streams, rivers, and ponds. Habitat loss, degradation, and fragmentation are some of the major threats to the species. Therefore, habitat restoration and management can be crucial in conserving the pike-topminnow and other species that depend on similar habitats.
Restoring and managing the habitat of the pike-topminnow can involve various techniques such as streambank stabilization, riparian zone restoration, and wetland creation. These measures help to improve the quality and quantity of suitable habitats, which can enhance the survival and reproduction of the species.
Research And Monitoring Programs
Research and monitoring programs are important for conserving and managing various fish species, including the pike-topminnow. These programs involve gathering data on the fish’s population size, distribution, and health, as well as studying their habitat and behavior.
This information helps scientists and managers make informed decisions about protecting and conserving the species. Some research and monitoring techniques include electrofishing, tagging and tracking, and genetic analysis. Government agencies, academic institutions, and conservation organizations often conduct these programs.
Conclusion
This spunky little fish may be small, but it packs a big punch regarding its importance in our aquatic ecosystems. From its bright, shimmering scales to impressive jumping abilities, the pike-topminnow is a unique and fascinating creature.
The pike-topminnow is a small but fascinating fish species native to North America. Its distinctive physical features, including its elongated body, sharp teeth, and vibrant colors, make it a popular research subject. And observation among aquatic enthusiasts and scientists.
Despite its popularity, however, the pike topminnow has faced significant threats to its survival. Habitat loss, pollution, and the introduction of non-native species have all contributed to the decline of the pike-topminnow population, prompting conservation efforts to protect and restore its natural habitats.
FAQs:
What Is The Habitat Of The Pike-Topminnow, And What Are Its Preferred Environmental Conditions?
The pike-topminnow’s natural habitat includes clear, cool streams and small to medium-sized rivers in North America. The species prefers shallow, slow-moving water with vegetation or rocky substrate and typically avoids areas with fast currents or sandy bottoms.
How Does The Pike-Topminnow Differ From Other Species Of Topminnows Regarding Physical Appearance And Behavior?
The pike-topminnow (Belonesox belizanus) is larger and has a more elongated body than other species of topminnows. It also has a distinctive dark stripe running along its side and a larger mouth.
What Is The Diet Of The Pike-Topminnow, And How Does It Obtain Its Food?
The pike-topminnow’s diet comprises small aquatic insects, crustaceans, and other small invertebrates. It obtains food using its sharp teeth and fast swimming abilities to catch prey in the water.
What Are The Threats To The Survival Of The Pike-Topminnow, And What Conservation Efforts Are Being Made To Protect The Species?
The threats to the survival of the pike-topminnow include habitat loss, degradation, and fragmentation due to human activities such as urbanization, agriculture, and mining. Pollution from agricultural runoff and other sources also threatens the species.
How Does The Pike-Topminnow Contribute To The Ecosystem, And What Is Its Role In The Food Chain?
The pike-topminnow, also known as the northern topminnow, is a small fish that primarily feeds on insects and other small aquatic organisms. It contributes to the ecosystem by serving as prey for larger fish and birds and controlling insect populations and other small organisms.

Aquarium passion is all about connecting with the aquatic life and providing education to the public on the importance of these creatures. We showcase a wide variety of marine life through our exhibits as well as working with schools to provide unique learning opportunities for students of all ages.