Acoustic tagging is a valuable tool for researchers who want to track the movements. And the behavior of fish in their natural habitats.
This technology works by attaching small acoustic tags to fish, which emit unique signals that underwater receivers can detect. By tracking these signals, researchers can gain valuable insights into different fish species’ behavior and migration patterns.
Acoustic tagging has become increasingly popular, allowing researchers. To gather data without disturbing the natural environment or altering the fish’s behavior. However, We will explain what acoustic tagging is and how it works.
We will also discuss 3 ways how to use acoustic tagging to track fish. Including transmitter detection and understanding prey movement. Additionally, we will look at the advantages and limitations of using acoustic tags for fish tracking. We will explore where you can use acoustic tags to track fish and the pros and cons of using this technology.

3 Ways On How To Use Acoustic Tagging To Track Fish
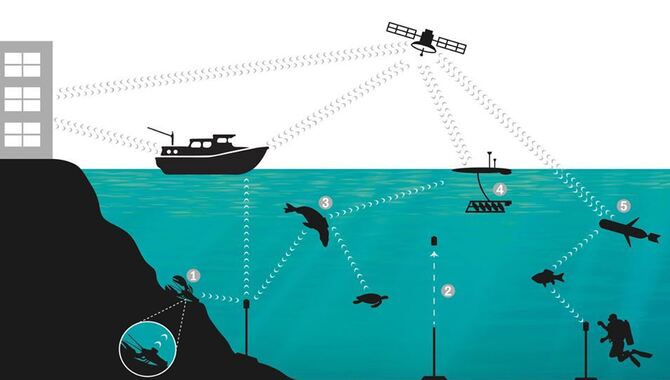
Acoustic tagging technology enables fisheries scientists to track individual fish over long distances in aquatic ecosystems. Scientists can detect its signal using hydrophone sensors placed. Underwater by attaching a small device, an acoustic tag that emits a unique sound.
Acoustic telemetry provides real-time fish movement patterns, habitat use, and behavior data. In addition to determining the type of acoustic transmitter or sensor that best suits environmental conditions. Scientists may need to triangulate their position using receiver arrays or listening stations.
Collaboration between researchers is essential for identifying new insights into fish populations and conservation efforts. Acoustic tagging is a valuable tool for tracking the movements and behavior of fish in their natural habitats. Here are 3 ways how to use acoustic tagging to track fish:
1. Transmitter Detection

Acoustic telemetry has become an essential tool for fisheries scientists worldwide studying fish populations and conservation efforts. Among all techniques, transmitter detection is the most popular method for tracking fish utilizing acoustic tags. Acoustic transmitters emit unique sounds that can detect by underwater listening stations/ receivers popular as hydrophones.
Researchers place multiple receivers in a body of water to track movement patterns. And habitat use of tagged fish and other marine animals such as turtles and mammals.
The technique allows scientists to gain new insights into individual fish movement patterns over long distances (kilometers) and its absence of data to examine environmental conditions, predation effects, prey abundance, survival rates, heart rate monitoring, stress levels, and fin or body cavity temperature measurements.
2. Understanding Prey Movement

To track fish using acoustic tagging, understanding prey movements is crucial. Researchers can study behavior, and conservation efforts. And fisheries management practices by attaching small transmitters to tagged fish and using underwater receivers to track their movements.
This allows for detailed maps of fish movement patterns and habitat use. Further advancements in acoustic telemetry, such as additional sensors. Allow for even more precise real-time tracking. Of marine animals like turtles and marine mammals over long distances.
3. Acoustics And Telemetry
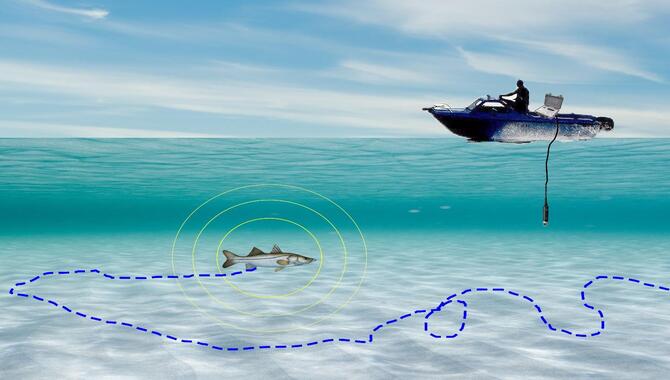
By utilizing acoustic transmitters and receivers placed strategically throughout the water column. Fisheries scientists can monitor tagged fish in real time using acoustic telemetry. This allows for detailed tracking of movement patterns and habitat use over long distances. Additionally, it provides new insights into individual fish behavior absent until now.
Factors such as tag type, frequency, background noise levels, and environmental conditions are critical to accuracy. And the range of acoustic telemetry signals received by submerged hydrophones or listening stations.
Advantages Of Acoustic Tagging
Acoustic tagging provides fisheries scientists with new insights into the behavior and movements of a wide range of marine animals; small transmitters or sensors attached to a fish’s fin or body cavity emit unique sounds picked up by hydrophones or receivers placed strategically on the ocean floor or a tracking vessel in real-time.
The tagged fish can then identify by triangulation or other techniques to monitor their location over time. Acoustic telemetry systems have proved highly effective in tracking salmon smolts and steelhead as they move from freshwater tributaries to the sea along thousands of kilometers of riverway.
Limitations Of Acoustic Tagging

Acoustic tagging is an invaluable technique in fisheries management and conservation efforts. While it provides new insights into fish behavior and movement patterns in aquatic ecosystems, the technology has some limitations that need addressing. The equipment for acoustic tagging is expensive and requires specialized training to use it effectively.
Additionally, acoustic tags have a limited battery life that necessitates frequent replacement and may be affected by environmental conditions like water temperature and turbidity that affect the range of acoustic signals. Nonetheless, fisheries scientists rely on this technology to gather real-time data on tagged fish using triangulation methods or listening stations installed on boats or in fixed locations.
How Does Acoustic Tagging Work?
Acoustic tagging is a technique used to track the movements and behavior of fish in their natural environment. The process involves attaching a small electronic tag to the fish that emits an acoustic signal, which can detect by receivers placed in the water. The tags can program to transmit signals at specific intervals or when triggered by certain behaviors, such as swimming through a particular area.
By analyzing the data collected from the tags, researchers can gain valuable insights into fish populations’ behavior and migration patterns. This information can inform fisheries management strategies and help protect endangered species. Acoustic tagging is a non-invasive method widely adopted by researchers worldwide, making it an essential tool in fisheries research and conservation efforts.
Where Can You Use Acoustic Tags To Track Fish?

Acoustic tagging is a powerful tool for tracking fish movements and behavior. Acoustic tags emit a unique sound that can be detected by receivers placed in the water, allowing researchers to track the fish’s location and movements over time.
However, acoustic tagging can be used in various aquatic environments, including rivers, lakes, and oceans. However, the locations where acoustic tagging is most effective will depend on the species being studied and their habitat preferences.
For example, some species may migrate long distances or move between different habitats, which may require different receivers or tagging techniques. It is essential to consult with experts in the field to determine the best approach for using acoustic tagging to track fish in your particular study area.
Pros And Cons Of Using Acoustic Tagging For Fish Tracking
![]()
Acoustic tagging is a valuable tool for tracking fish populations and behavior. Researchers can monitor their movements by attaching small acoustic transmitters to individual fish and gather important data on their habitat use, migration patterns, and survival rates.
However, like any technology, there are pros and cons to using acoustic tagging for fish tracking. Some advantages include its non-invasive nature, which allows fish to be tracked without harming or disrupting their natural behaviors. Additionally, acoustic tags can transmit data over long distances and in various aquatic environments.
On the other hand, there are also some potential drawbacks to using acoustic tagging. The cost of equipment and personnel needed for acoustic tagging can be high, which may limit its use in some research projects. Additionally, some studies have shown that tagged fish may experience changes in behavior or activity levels due to the presence of the tag. Despite these challenges, acoustic tagging remains an essential fisheries research and management tool.
Conclusion
Acoustic tagging is a powerful tool for tracking fish behavior and movements. By attaching small tags to fish and using underwater receivers to detect the signals emitted by these tags, researchers can gain valuable insights into the ecology of these aquatic creatures.
This technology has been used to study everything from migration patterns to feeding habits and has even helped identify critical habitats for endangered species. While acoustic tagging requires specialized equipment and expertise, it is an increasingly popular method among fisheries scientists worldwide.
As our understanding of fish behavior evolves, we can expect acoustic tagging to play an essential role in shaping our approach to conserving and managing these vital marine resources. We hope you now understand how to use acoustic tagging to track fish.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can I Use Acoustic Tagging To Track Fish?
Acoustic tagging requires implanting a small device that emits sound waves into fish, which can be tracked using hydrophones. This method offers valuable insights into fish behavior and migration patterns but must carefully consider ethical concerns and potential harm to the fish.
What Is Acoustic Tagging, And Why Do You Need It?
Acoustic tagging involves using sound signals to track fish movements by attaching a small tag with an acoustic transmitter to the fish. This method helps researchers understand fish behavior, migration patterns, and habitat use by recording the location of the fish through a receiver that picks up the signal emitted by the tag.
Where Can I Find An Acoustic Tag For A Particular Species Of Fish?
Check the manufacturer’s website or contact local fisheries and research organizations to find an acoustic tag for a specific fish species. Consider the appropriate frequency and battery life for your needs and follow proper tagging protocols while obtaining necessary permits before starting your research.
Is It Possible To Make Your Acoustic Tags From Materials Readily Available In Nature, Like Wood Or Twigs?
While it may seem feasible to create acoustic tags from natural materials, it is not recommended due to the precise engineering and calibration required for proper function. Homemade tags could harm fish and lead to inaccurate data collection. It is best to purchase pre-made acoustic tags from trustworthy manufacturers.
What Types Of Fish Can Be Tracked With Acoustic Tagging?
Acoustic tagging can track various fish species, such as salmon, tuna, sharks, and sturgeon. The type of tag used depends on the fish’s size and behavior. Acoustic tags offer insight into movement patterns, migration routes, and habitat use. Ongoing research is exploring the potential uses of acoustic tagging in fisheries management.

Aquarium passion is all about connecting with the aquatic life and providing education to the public on the importance of these creatures. We showcase a wide variety of marine life through our exhibits as well as working with schools to provide unique learning opportunities for students of all ages.








